This history book offers excellent images but skimps on modern science

Books about the history of science, like many other histories, must contend with the realization that others have come before. Their tales have already been told. So such a book is worth reading, or buying, only if it offers something more than the same old stories.
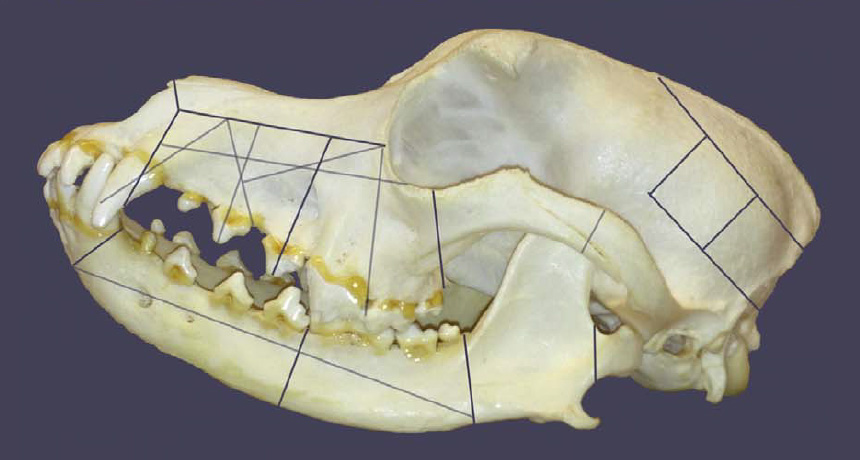
In this case, The Oxford Illustrated History of Science offers most obviously an excellent set of illustrations and photographs from science’s past, from various ancient Egyptian papyruses to the Hubble Space Telescope’s ultradeep view of distant galaxies. Some of the images will be familiar to science fans; many others are obscure but apt; nearly all help illustrate various aspects of science’s history.
And yet the pictures, while many may be worth more than 10,000 words, are still just complements to the text. Oxford attempts a novel organization for recounting the story of science: a sometimes hard-to-follow mix of chronological and topical. The first section, “Seeking Origins,” has six chapters that cover ancient Mediterranean science, science in ancient China, medieval science (one chapter for the Islamic world and Europe, one for China), plus the scientific revolution and science in the Enlightenment. The second section, “Doing Science,” shifts to experimenting, fieldwork, biology, cosmology, theory and science communication.
Each chapter has a different author, which has the plus of bringing distinct expertise to each subject matter but the minus of vast divergence in readability and caliber of content. Some chapters (see “Exploring Nature,” on field science) are wordy, repetitive and lack scientific substance. Others (“Mapping the Universe”) are compelling, engaging and richly informative. A particularly disappointing chapter on biology (“The Meaning of Life”) focuses on 19th century evolution, with only a few paragraphs for the life science of the 20th and 21st centuries. That chapter closes with an odd, antiscientific tone lamenting the “huge numbers of people … addicted to antidepressants” and complaining that modern biology (and neuroscience) “threatens to undermine traditional values of moral responsibility.”
Some of the book’s strongest chapters are the earliest, especially those that cover aspects of science often missing in other histories, such as science in China. Who knew that the ancient Chinese had their own set of ancient elements — not the Greeks’ air, earth, water and fire, but rather wood, fire, water, soil and metal?
With the book’s second-half emphasis on how science was done rather than what science found out, the history that emerges is sometimes disjointed and out of order. Discussions of the modern view of the universe, which hinges on Einstein’s general theory of relativity, appear before the chapter on theory, where relativity is mentioned. In fact, both relativity and quantum theory are treated superficially in that chapter, as examples of the work of theorists rather than the components of a second scientific revolution.
No doubt lack of space prevented deeper treatment of science from the last century. Nevertheless the book’s merits outweigh its weaknesses. For an accessible account of the story of pre-20th century science, it’s informative and enjoyable. For more recent science, you can at least look at the pictures.